5 Things to Look For When Buying a Portable Power Station
time2023/02/06
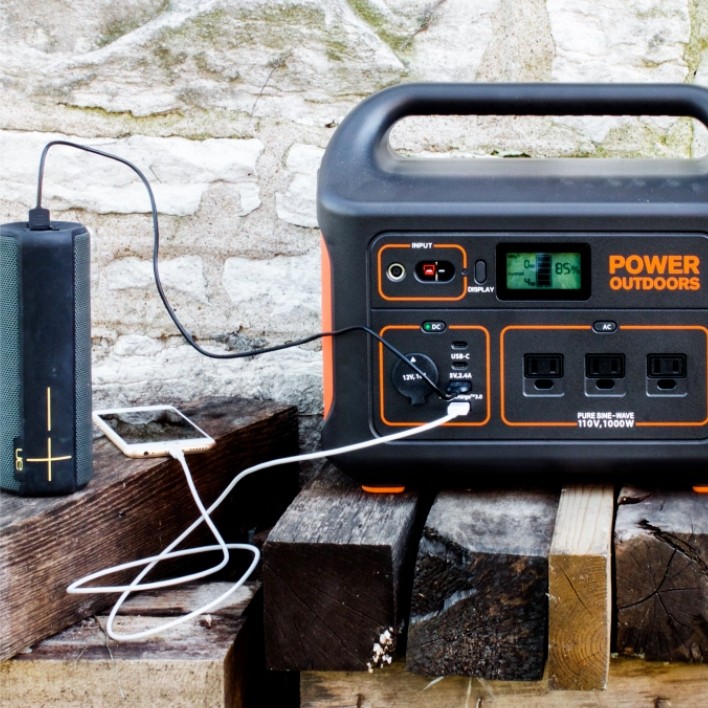

- Portable power stations are quieter, lighter, and don't require fuel to start delivering power. To help you find a quality power plant, here's what you should look for when buying a new power plant.

With advances in battery technology, portable power stations have enough capacity and raw power to reliably power electronic devices that require much more power than ordinary power banks can provide. While not as powerful as gas generators, they are quieter, lighter, and don't require fuel to start providing electricity.
So if you're looking for a quiet mobile device to power your smartphone, laptop, computer or TV, buying a portable power station might be a better solution. To help you find a quality power plant, here are five things you should be aware of when shopping for a new power plant.
1. Battery Capacity
When looking for a portable power station, battery capacity is the most important specification you should be looking for. The larger the battery capacity, the longer you can run your device per charge. So, in general, buy the battery with the largest capacity possible.
However, given size, weight, and cost, you may wish to take a more calculated approach when considering battery capacity for a portable power station.
Knowing battery capacity can be confusing since different manufacturers use different metrics to measure the battery capacity of their portable power stations. The most common metrics used to measure battery capacity include mAh (milliampere-hours), Ah (ampere-hours), Wh (watt hours), and kWh (kilowatt hours).
Electronic devices usually indicate their maximum power consumption in watt-hours, which you can find on various types of power supplies. If a power supply is rated in watts, remember that one watt equals one watt-hour.
To better understand how long a portable power station can power your devices, you first need to know its battery capacity (measured in watt-hours). You can do this by looking at its watt-hour rating. But if it's just stating the battery's capacity in mAh (milliamp hours) or Ah (ampere-hours), you can add those numbers to its rated system voltage (12v or 24v) and use the chart below to find its watt-hour rating:
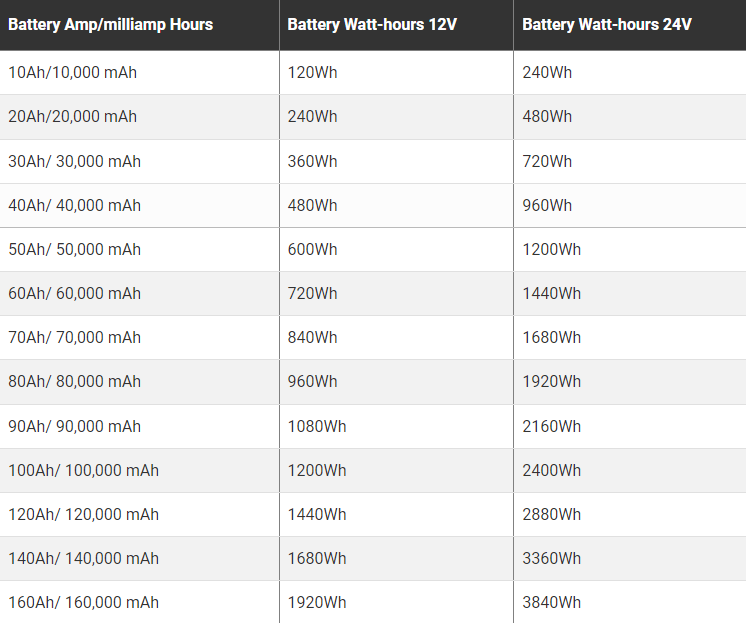
So let's say your laptop is rated to run at a maximum of 90W or 90Wh, and your portable power station has a battery capacity of 40,000 mAh on a 12-volt system. Using the table above, you'll see that the power station has a battery capacity of 480Wh. If you divide that by the 90Wh the laptop uses, you can expect roughly 5 hours of runtime, regardless of power draw and other variables.
2. Battery Technology
Another important factor you should look for in a portable power station is the battery technology or the type of battery it uses. The type of battery used in a portable power station largely determines the size, weight, cost, charging speed, and how long your power station can continue to generate AC power before it cuts off.
Lithium-ion (Li-Ion), lithium-polymer (Li-Po), and lead-acid batteries are the most commonly used batteries in portable power stations.
Lithium-ion batteries charge three times faster than lead-acid batteries and have the highest energy density of the three. Li-polymer batteries, on the other hand, have lower energy density than Li-ion batteries, but have fast charging capabilities and are generally safer to use than Li-ion and lead-acid batteries. While lead-acid batteries are the most affordable of the three, they are bulky, slow to charge, and have the lowest energy density.
If you're looking for something that's packable, lighter, and lasts a lot, lithium-ion batteries are usually a worthwhile investment. However, if you want something that is safer, charges quickly, and has the lowest passive discharge rate, a LiPo battery power station is probably a better choice.
Lead-acid batteries are generally not recommended, but if you really need an inexpensive plug-and-play backup power station for emergency use, a lead-acid power station will suffice.
3. Frequency Conversion Technology
Depending on the devices you'll be powering, having the right inverter in your portable power station can keep your delicate equipment safe from damage and keep them working as efficiently as possible, saving battery power.
A power inverter is an electronic component that converts a battery's direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). Direct current is used to charge battery-operated handheld devices such as cell phones, tablets, and Bluetooth headsets, while alternating current is used to power more power-hungry devices such as laptops, computers, TVs, and game consoles.
Generally, there are two types of inverters; they are pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters. A pure sine wave inverter provides a clean sine wave that produces alternating current, while a modified sine wave inverter uses pulse width modulation (PWM), which produces an electrical signal that attempts to mimic a pure sine wave signal.
If you are powering delicate and highly sensitive equipment, then a pure sine wave inverter should be your only choice. However, if you're only going to use your power station to power computers, monitors, consoles, and TVs, then a power station with a modified sine wave inverter should work just fine while saving you quite a bit of money.
4. Peak and Continuous Power
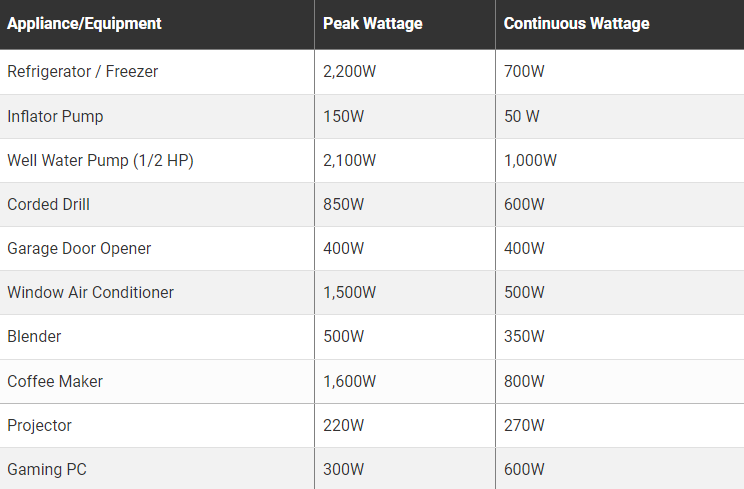
Peak and continuous power are also important specifications you should be looking for when shopping for a portable power station. While portable power stations are commonly used to power computers, televisions, and other electronics, they can also power refrigerators, corded power tools, fans, and kitchen appliances like blenders and food processors. However, these devices can only be powered by portable power stations if they have sufficient peak and continuous power.
Most power-hungry appliances and devices require a certain peak or surge of power to start and turn them on quickly. Once turned on, they will require a lower but continuous power supply, called continuous watts or rated watts.
To find out how many peaks and continuous power your portable power station needs, here is a list of typical devices and their power ratings:
5. Power Input and Output Ports
When it comes to portable power stations, you can never find enough ports to charge and power your devices. This is especially true for DC-powered charging ports since you can always use an extension cord to get more AC outlets.
We recommend equipping your handheld with a portable power station with multiple USB and USB-C charging ports, a 12 V charging port for Internet routers, and at least 2 AC power outlets. If you plan to store the plant in the car, you may also need Anderson telephone poles.
After looking at all of the charging ports and outlets for your portable power station, you should also look for the ports used to charge the power station. These will include your regular AC, DC, and solar charging ports as well as an Anderson power pole for charging in your car.
Get the Functionality You Need Before Doing Anything Extra
Many companies are trying to add more and more features to their portable power stations to entice you to buy their product. But before you go shopping for a portable power station with NFC and wireless charging, make sure it meets your needs first. Doing so will ensure that you get a durable and reliable power station that can power your equipment when needed.
The above briefly introduces the matters needing attention when choosing a portable power station. If you want to buy a portable power station, please contact us.
ACCMercado provides professional consumer electronics solutions. Our services are based on 20 years of mature industry experience, and we cooperate with various powerful partners to meet the regional needs of global customer brands and provide professional one-stop third-party brand customization services. We can provide you with wholesale options on all products to suit your specific business needs and save you money with our competitive discount rates on high-volume orders.
